React 体系的懒加载方案及其原理
目录
问题的产生
代码分割是目前非常流行的前端技术。随着前端工程的日益复杂,引入了很多第三方库,代码体积也变得越来越大,我们需要合理的管理我们的资源包。
使用代码分割技术,将一个大的代码包拆分成多个小包,这个在页面前期只需要加载必须的资源,非必须的资源可以放在后期需要的时候再加载。比如有些模块用户可能都不会点击,只有等点击的时候才加载。这种懒加载可以显著提高页面早期的速度,提高性能体验。
所以我们需要寻求好的懒加载方案。
方案比较
在 React 体系中,目前有这几种方案可以选择:
- import()
- React.lazy
- @loadable/component
- react-loadable
动态导入
动态导入 import() 是 es 原生支持的的一个方案。
import() 的优势是可以运行时加载模块,这样就能补齐 es import 命令的缺陷。因为相比于 CommonJS 的 require 可以动态加载脚本,import 命令是静态编译,在代码编译阶段就将模块关系确定了,所以这样的代码是毫无意义的:
// 报错
if (x === 2) {
import MyModual from './myModual';
}有了 import(),就能动态加载脚本,在使用上非常灵活。
// a.js
export default function Add() {
...
}
// b.js
if (x === 2) {
import('./a.js')
.then(module => {
const Add = module.default
Add()
})
}更重要的是执行 import() 返回的是 Promise,是一个异步的模块,也可以用 async 函数对其管理:
async function main() {
const myModule = await import('./myModule.js');
const {
export1,
export2
} = await import('./myModule.js');
const [
module1,
module2,
module3
] = await Promise.all([
import('./module1.js'),
import('./module2.js'),
import('./module3.js')
])
}
main();不过缺点在于,import() 语法很新,老的浏览器可能不会兼容。通过 Webpack + Babel 会将 import() 转换为 Promise + domcument.createElement('script') 的方式(针对于 web 端)。
React.lazy
React.lazy 是 React 官方提供的一个代码分割方案。相比于import(),React.lazy 是针对于 React 组件的一个代码分割方案,需要配合 Suspense 使用:
import React, { Suspense } from 'react';
import MyErrorBoundary from './MyErrorBoundary';
const OtherComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./OtherComponent'));
const AnotherComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./AnotherComponent'));
const MyComponent = () => (
<div>
<MyErrorBoundary>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<section>
<OtherComponent />
<AnotherComponent />
</section>
</Suspense>
</MyErrorBoundary>
</div>
);优势上 React.lazy 是原生组件,可以搭配 ErrorBoundary 特性,容错上也更好。
缺点在于目前 React.lazy 和 Suspense 技术还不支持服务端渲染。所以如果要在服务端上使用懒加载,可以使用 @loadable/component 这个库。
@loadable/component
@loadable/component 是社区版的一个代码分割方案,简单好用。
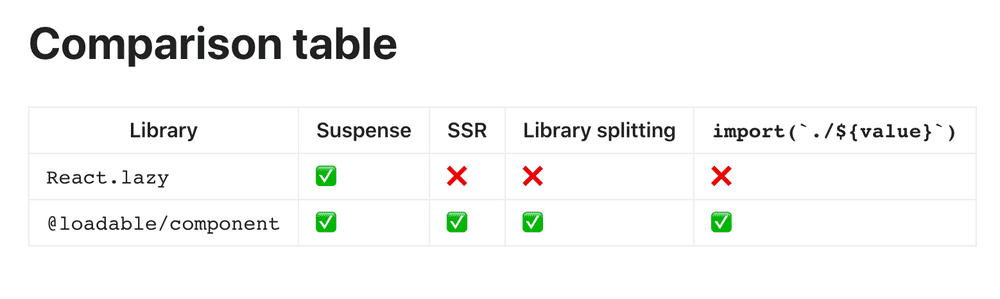
它相比于 React.lazy,最大的区别是支持服务端渲染。以及它跟 React.lazy 不冲突,还能使用 Suspense 特性,可以看作是 React.lazy 的一个增强版本:
使用上非常简单:
import React, { Suspense } from 'react'
import { lazy } from '@loadable/component'
const OtherComponent = lazy(() => import('./OtherComponent'))
function MyComponent() {
return (
<div>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<OtherComponent />
</Suspense>
</div>
)
}react-loadable
react-loadable 是另一个代码分割的方案,只不是这个库相比于 比较老,官网的介绍是这样的:
A higher order component for loading components with dynamic imports.
可以简单看一下:
import Loadable from 'react-loadable';
import Loading from './my-loading-component';
const LoadableComponent = Loadable({
loader: () => import('./my-component'),
loading: Loading,
});
export default class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return <LoadableComponent/>;
}
}react-loadable 属于上一代的方案,它很早就不维护了,不兼容 Webpack v4+ and Babel v7+。所以在目前的实践中还是考虑上面三种方案。
原理
@loadable/component
这里研究一下 @loadable/component 这个库的源码。@loadable/component 其实是 @loadable 下的一个包,还有 @loadable/server、 @loadable/babel-plugin、@loadable/webpack-plugin 等包,是为服务端渲染而准备的,纯前端应该用不太到。目前只研究 @loadable/component。
下载 @loadable/components 源码,可以看到它的目录结构:
最重要的部分是在 createLoadable.js 中:
function createLoadable({
defaultResolveComponent = identity,
render,
onLoad,
}) {
function loadable(loadableConstructor, options = {}) {
const ctor = resolveConstructor(loadableConstructor)
const cache = {}
// 获取缓存的 key,key 发生改变的时候会 reload 新资源
function getCacheKey(props) {}
// 将加载进来的模块通过 options.resolveComponent 取出模块
function resolve(module, props, Loadable) {}
// 内部主类
class InnerLoadable extends React.Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
const cacheKey = getCacheKey(props)
return {
...state,
cacheKey,
// key 的改变会触发新的 render 流程
loading: state.loading || state.cacheKey !== cacheKey,
}
}
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
result: null,
error: null,
loading: true,
cacheKey: getCacheKey(props),
}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.mounted = true
// 获取缓存
const cachedPromise = this.getCache()
// 如果 promise 状态是失败的,则清理
if (cachedPromise && cachedPromise.status === STATUS_REJECTED) {
this.setCache()
}
// 当还在 loading 的时候,则 loadAsync
if (this.state.loading) {
this.loadAsync()
}
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
// 只在 key 变更后才触发变化
if (prevState.cacheKey !== this.state.cacheKey) {
this.loadAsync()
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.mounted = false
}
safeSetState(nextState, callback) {
if (this.mounted) {
this.setState(nextState, callback)
}
}
getCacheKey() {
return getCacheKey(this.props)
}
getCache() {
return cache[this.getCacheKey()]
}
setCache(value = undefined) {
cache[this.getCacheKey()] = value
}
triggerOnLoad() {
if (onLoad) {
setTimeout(() => {
onLoad(this.state.result, this.props)
})
}
}
// 同步加载模块,在一些场景有用,比如 node 端(webpack target=node)
loadSync() {}
// 核心:异步加载模块,加载和解析过程分解的
loadAsync() {
const promise = this.resolveAsync()
promise
.then(loadedModule => {
const result = resolve(loadedModule, this.props, { Loadable })
this.safeSetState(
{
result,
loading: false,
},
() => this.triggerOnLoad(),
)
})
.catch(error => this.safeSetState({ error, loading: false }))
return promise
}
// 核心:异步解析模块
resolveAsync() {
const { __chunkExtractor, forwardedRef, ...props } = this.props
let promise = this.getCache()
if (!promise) {
// requireAsync 就是使用中用到的 () => import('./'),它会返回一个 promise
promise = ctor.requireAsync(props)
promise.status = STATUS_PENDING
this.setCache(promise)
promise.then(
() => {
promise.status = STATUS_RESOLVED
},
error => {
promise.status = STATUS_REJECTED
},
)
}
return promise
}
// render 函数,其实就是 React 组件的 render,没有啥特别的
render() {
const {
forwardedRef,
fallback: propFallback,
__chunkExtractor,
...props
} = this.props
const { error, loading, result } = this.state
// suspense 功能配置
if (options.suspense) {
const cachedPromise = this.getCache() || this.loadAsync()
if (cachedPromise.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
throw this.loadAsync()
}
}
// 错误则 throw
if (error) {
throw error
}
// 兜底 loading
const fallback = propFallback || options.fallback || null
if (loading) {
return fallback
}
return render({
fallback,
result,
options,
props: { ...props, ref: forwardedRef },
})
}
}
// 这里是对于 InnerLoadable 做一些增强功能,包括转发 ref
const EnhancedInnerLoadable = withChunkExtractor(InnerLoadable)
const Loadable = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => (
<EnhancedInnerLoadable forwardedRef={ref} {...props} />
))
// preload 功能
Loadable.preload = props => ctor.requireAsync(props)
return Loadable
}
function lazy(ctor, options) {
...
}
return { loadable, lazy }
}
export default createLoadable整体阅读下来不难,就是一个 React 组件,内部去调用 loadAsync(),帮开发者去管理懒加载资源,本质上还是跑 import() 命令,在 Webpack 的编译下,也是 Promise + document.createElement('script') 这一套。
lazy 部分的函数我没有研究,因为这个需要深入看一下 React.lazy 和 Suspense 的东西,所以先放一放,后续有需要再说。